Final ID: MDP1287
Development of a Sitosterolemia Risk Prediction Scale (SRPS): A Screening Tool
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Sitosterolemia, a hereditary disorder marked by elevated plant sterol levels, presents diagnostic challenges due to its similarity to other lipid disorders. The development of the Sitosterolemia Risk Prediction Scale (SRPS) aims to address this by synthesising genetic, clinical, and dietary data into a coherent risk assessment model.
Research Question: We propose that a structured risk scale, integrating diverse factors known to affect sitosterolemia, can significantly improve the accuracy of predicting the disorder. The SRPS is hypothesised to facilitate early detection and inform targeted interventions.
Aim: The primary aim is to conceptualise and outline the SRPS, which categorises individuals into risk categories based on a point system reflecting genetic predispositions, clinical symptoms, dietary habits, and response to treatments. This scale seeks to enhance the clinical identification of sitosterolemia, promoting timely and personalised management strategies.
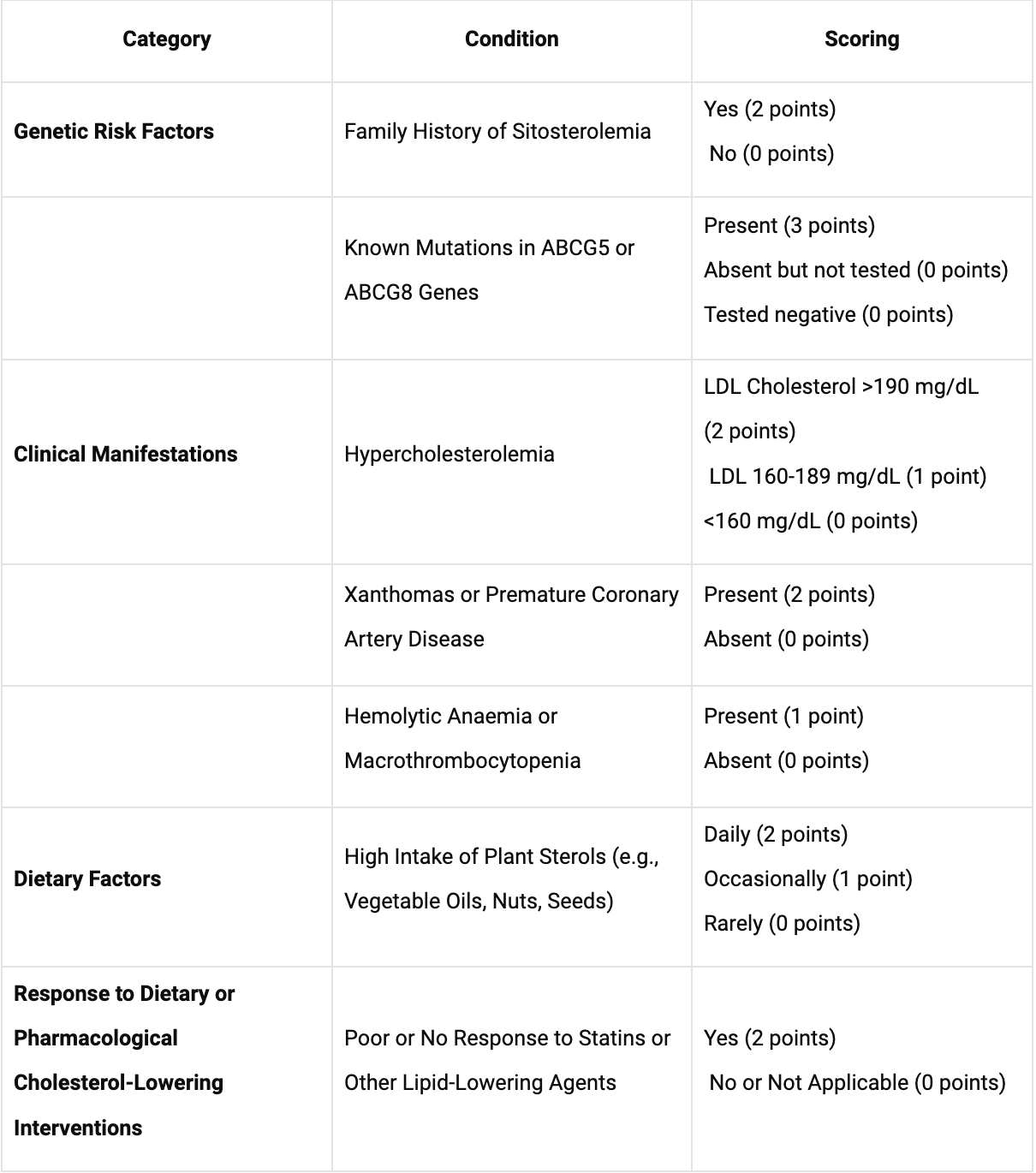
Methods: A detailed table was generated to present the SRPS, categorising risk factors into genetic, clinical, dietary, and response to treatment. This innovative method allowed for the efficient synthesis and visualisation of complex data.
Results: The SRPS table methodically organizes risk factors into low (0-2 points), moderate (3-5 points), and high (6+ points) categories. This stratification guides further diagnostic actions, ranging from exploring alternative causes of hyperlipidemia to necessitating comprehensive genetic and lipid analyses.
Conclusion:The SRPS represents an innovative framework for assessing sitosterolemia risk, highlighting the potential benefits of integrating genetic, clinical, and dietary information. It further underscores the importance of a multifactorial approach in the early detection and management of sitosterolemia.
Research Question: We propose that a structured risk scale, integrating diverse factors known to affect sitosterolemia, can significantly improve the accuracy of predicting the disorder. The SRPS is hypothesised to facilitate early detection and inform targeted interventions.
Aim: The primary aim is to conceptualise and outline the SRPS, which categorises individuals into risk categories based on a point system reflecting genetic predispositions, clinical symptoms, dietary habits, and response to treatments. This scale seeks to enhance the clinical identification of sitosterolemia, promoting timely and personalised management strategies.
Methods: A detailed table was generated to present the SRPS, categorising risk factors into genetic, clinical, dietary, and response to treatment. This innovative method allowed for the efficient synthesis and visualisation of complex data.
Results: The SRPS table methodically organizes risk factors into low (0-2 points), moderate (3-5 points), and high (6+ points) categories. This stratification guides further diagnostic actions, ranging from exploring alternative causes of hyperlipidemia to necessitating comprehensive genetic and lipid analyses.
Conclusion:The SRPS represents an innovative framework for assessing sitosterolemia risk, highlighting the potential benefits of integrating genetic, clinical, and dietary information. It further underscores the importance of a multifactorial approach in the early detection and management of sitosterolemia.
More abstracts on this topic:
3-Mercaptopyruvate Sulfurtransferase is a Critical Regulator of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Catabolism in Cardiometabolic HFpEF
Li Zhen, Doiron Jake, Xia Huijing, Lapenna Kyle, Sharp Thomas, Yu Xiaoman, Nagahara Noriyuki, Goodchild Traci, Lefer David
A human cardiomyocyte model of CD36 haploinsufficiency uncovers fatty acid oxidation deficits driving dilated cardiomyopathyAl Sayed Zeina, Klattenhoff Carla, Aragam Krishna, Ellinor Patrick, Willcox Jon, Zheng Alice, Koledova Vera, Srivastava Salil, Yin Xiaofei, Chaffin Mark, Rigaud Vagner, Kovacs-bogdan Erika